RUPTURE DE LA COIFFE DES ROTATEURS / ROTATORS CUFF RUPTUR
Les mouvements répétitifs des membres supérieurs ou l'usure naturelle peuvent entraîner une rupture de la coiffe des rotateurs. Ces tendons, qui permettent une bonne mobilité de l'épaule, se rompent en raison du frottement régulier contre l'os acromion.
Les tendinites de la coiffe des rotateurs touchent surtout les patients sportifs et ceux qui exercent une profession manuelle.
Elles sont causées par un conflit mécanique entre la voûte sous acromiale et les tendons de la coiffe des rotateurs.
Il est fondamental de comprendre que tout déséquilibre entre la coiffe des rotateurs et le deltoïde, lors des mouvements d’abduction-rotation interne, aboutira à un frottement de la coiffe des rotateurs sur la voûte acromiocoracoïdienne à travers la bourse sous-acromiodeltoïdienne.
Le même geste mille fois répété conduira à une défaillance fonctionnelle de cette bourse et à une usure de la coiffe sur les structures ostéo-ligamentaires.
La pathologie dégénérative de l’épaule commence toujours par une atteinte type « tendinite » pouvant aller jusqu’à la rupture du tendon.
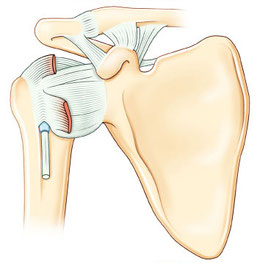
3 os
la clavicule
l’omoplate
l’humérus
5 articulations
- l’articulation gléno-humérale
- l’articulation sous-acromiale
- l’articulation acromio-claviculaire
- l’articulation sterno-claviculaire
- l’articulation scapulo-thoracique

Repetitive movements of the upper limbs or natural wear can lead to rotator cuff tear. These tendons, which enable good shoulder mobility, rupture as a result of regular rubbing against the acromion bone.
Rotator cuff tendonitis affects mainly sports patients and those who work in manual occupations.
It is caused by a mechanical conflict between the subacromial arch and the rotator cuff tendons.
It is fundamental to understand that any imbalance between the rotator cuff and the deltoid, during abduction-internal rotation movements, will result in the rotator cuff rubbing against the acromiocoracoid arch through the subacromiodeltoid bursa.
The same action, repeated a thousand times, will lead to functional failure of this bursa and wear and tear of the cuff on the osteo-ligamentary structures.
The degenerative pathology of the shoulder always starts with a "tendonitis" type of damage that can go as far as the rupture of the tendon.
3 bones
- the clavicle
- the scapula
- the humerus
5 joints
- the glenohumeral joint
- the subacromial joint
- the acromioclavicular joint
- the sternoclavicular joint
- the scapulo-thoracic joint

Reprogrammation posturale / Postural reprogramming
Une récupération de la mobilité passive et active :
- Etirement de la capsule avec le Gyrotonic ou le Cadillac.
- Renforcement des stabilisateurs locaux avec le Reformer ou Gyrotonic ou le petit matériel.
- Renforcement des stabilisateurs globaux avec le Reformer ou Gyrotonic.
- Mobilisation de l'articulation de l'épaule et des mobilisateurs globaux avec le Reformer ou Gyrotonic ou le Gyrotoner.
A recovery of passive and active mobility:
- Stretching of the capsule with the Gyrotonic or the Cadillac.
- Strengthening of the local stabilizers with the Reformer or Gyrotonic or small equipment.
- Strengthening of the global stabilizers with the Reformer or Gyrotonic.
- Mobilization of the shoulder joint and global mobilizers avec le Reformer ou Gyrotonic or the Gyrotoner.
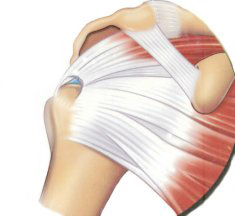
les muscles de la coiffe des rotateurs / The muscles of the rotators cuff



